Installation & Deployment¶
Shield can be installed in 2 main methods:
- Using the Installation Scripts (can be used for Ubuntu and CentOS)
- Using the OVA file (for CentOS)
Shield components are deployed on Linux machines using Rancher. Rancher is a well-known software platform that enables easy deployment and management of Docker and Kubernetes products in production environments.
First step is to create the Kubernetes cluster (using Rancher) and once the cluster is ready - deploy Shield on it.
The recommendation is to set up a dedicated Linux machine which will be used for cluster deployment and management. This machine will be referred to as the Rancher Server machine. This machine will also include the Kubectl & Helm on it (see below). The Rancher Server can be a separated machine or on one of the Master machines (running etcd & Control Plane).
For High Availability deployments, 3 Master (cluster management) machines are required.
The process detailed below is dedicated to installing using the Installation Scripts. When installing using the OVA, some steps can be skipped (due to the components that are included in the OVA). For detailed instructions on installing using the OVA go here.
Note
The process detailed below includes steps performed both on the Linux machine(s) and on the Rancher user interface (using a browser).
The steps describe where it takes place (either in Rancher or Linux).
Prepare The Linux Machines¶
Each Linux machine that takes part in the Shield cluster must be prepared before creating the cluster. Please follow these steps and perform them on each machine separately:
Note
When using Ubuntu 16.04 for a Kubernetes system, some steps are needed for Kubernetes to run successfully. For more details, go here.
Configure OS settings:
curl -s -o configure-sysctl-values.sh https://raw.githubusercontent.com/EricomSoftwareLtd/Shield/Rel-19.09.4/Kube/scripts/configure-sysctl-values.sh
chmod +x configure-sysctl-values.sh
sudo ./configure-sysctl-values.sh
Install Docker:
curl -s -o install-docker.sh https://raw.githubusercontent.com/EricomSoftwareLtd/Shield/Rel-19.09.4/Kube/scripts/install-docker.sh
chmod +x install-docker.sh
./install-docker.sh
Add current user to the docker group:
sudo usermod -aG docker "$USER"
Logout and login again.
Verify that Docker is installed properly:
docker version
All the machines should be synchronized. Configure the NTP (Network Time Protocol) and the timezone on the machine.
Repeat these steps for each machine in the system.
Note
When installing Shield on CentOS, it is required to stop firewalld prior to proceeding with the deployment process. Run:: sudo systemctl stop firewalld sudo systemctl disable firewalld
Create The Cluster¶
Once all Shield machines are ready, select a machine to be the Rancher Server to init Rancher and form the cluster.
Note
For High Availability - Shield cluster must include 3 Master (cluster management) machines
Deploy Rancher¶
On the Linux Rancher Server machine, create a dedicated folder and run Rancher:
mkdir ~/ericomshield
curl -s -o run-rancher.sh https://raw.githubusercontent.com/EricomSoftwareLtd/Shield/Rel-19.09.4/Kube/scripts/run-rancher.sh
chmod +x run-rancher.sh
./run-rancher.sh
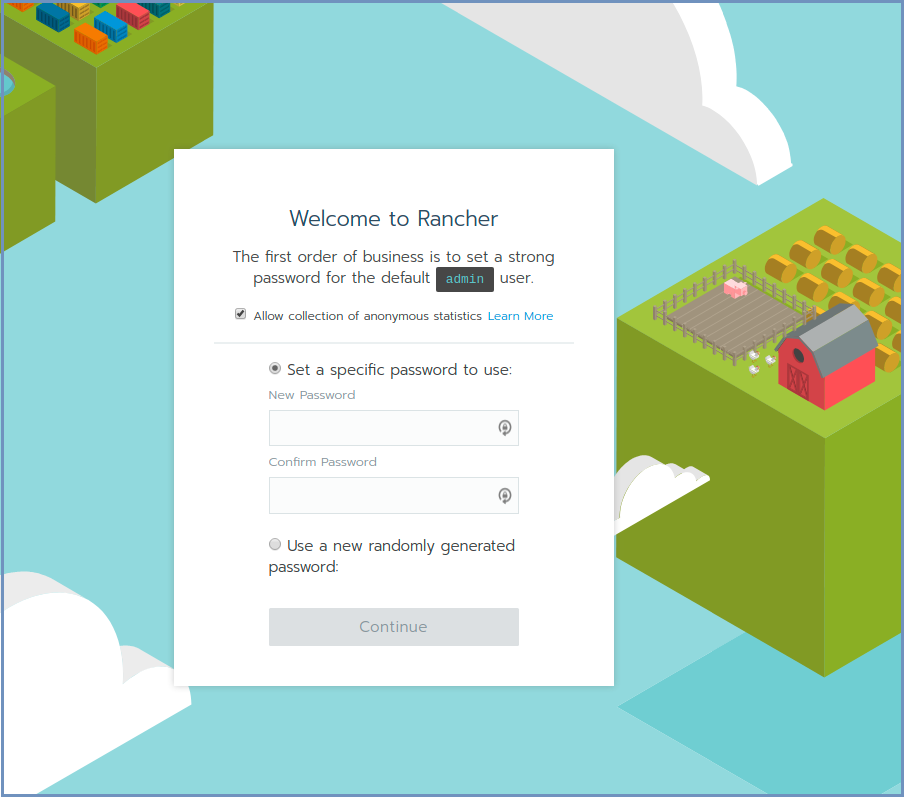
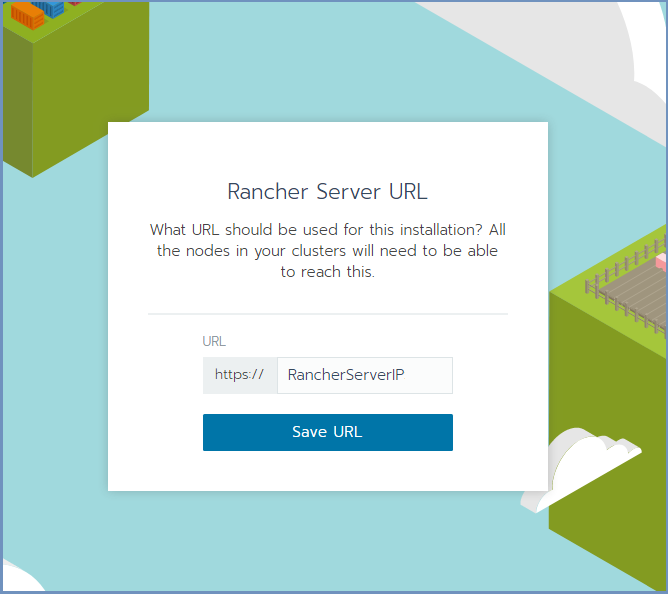
Init Rancher - Open a browser and go to https://RancherServerIPAddress:8443 (using the Rancher Server IP address).
Set the administrator password (as desired) and click Continue
Click Save URL.
Form A Cluster & Add Nodes¶
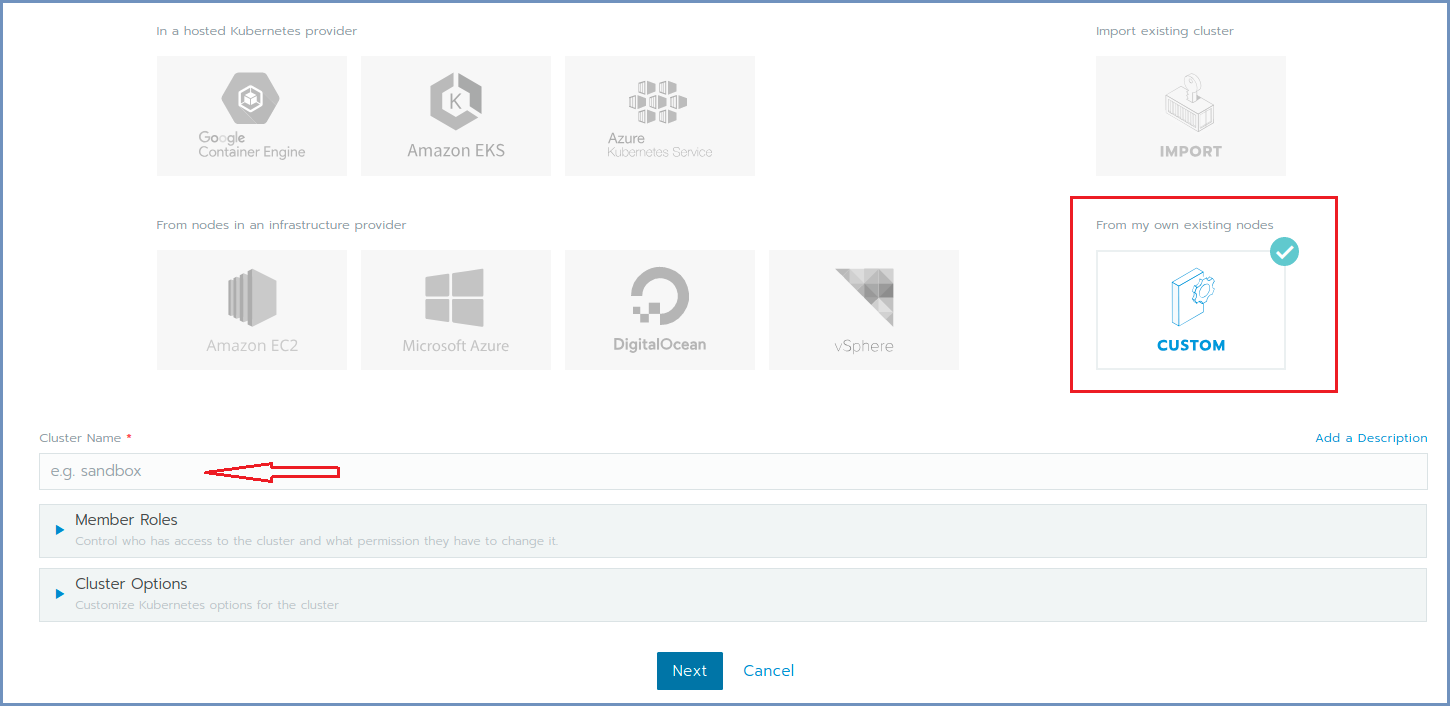
In Rancher, click the Add Cluster option (on the right).
Fill in the Cluster Name.
Expand the Cluster Options and on the Network Provider select the Flannel option. Click Next.
Select the required check boxes.
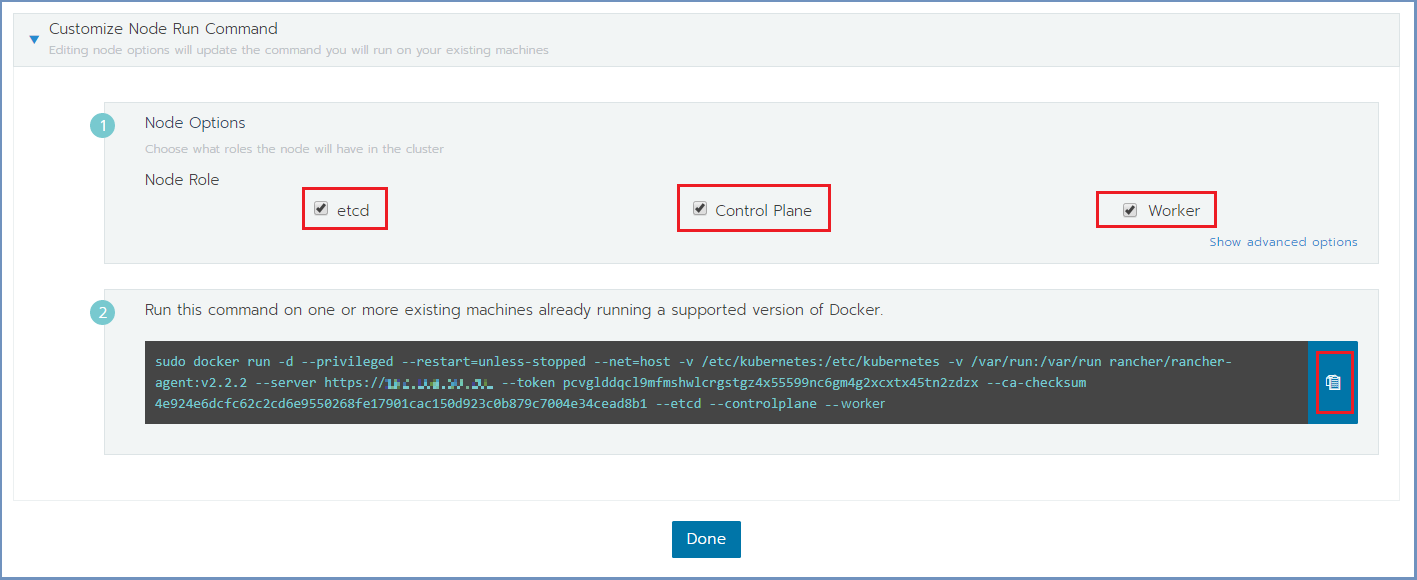
For a Cluster Management node (Master machine), select all check boxes. For Worker node, select the Worker check box. E.g.,:
Copy the command on the bottom (using the Copy to Clipboard option in the right).
Run the copied command on EACH Linux machine to join it to the cluster. Make sure the copied command matches the
node to join (Master/Worker). Follow the node joining by clicking on Nodes in the cluster menu.
Wait until the process is finished. After the node is joined to the cluster, a green message appears at the bottom of the page.
Repeat this process per each node until the cluster is complete. Click Done.
Set Node Labels¶
According to the planned deployment, set the node labels for each machine:
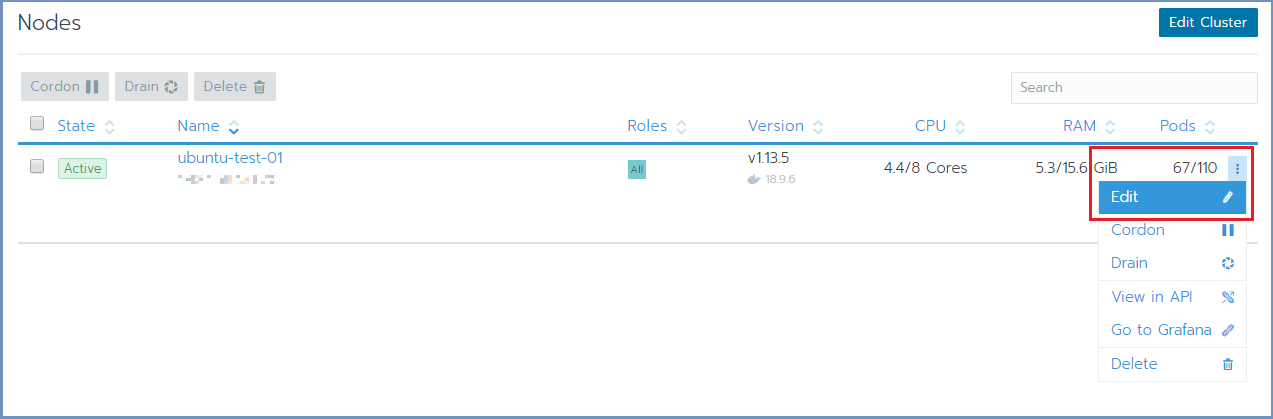
In Rancher, select Nodes and for each node you wish to edit, select the Edit option from the menu on the right
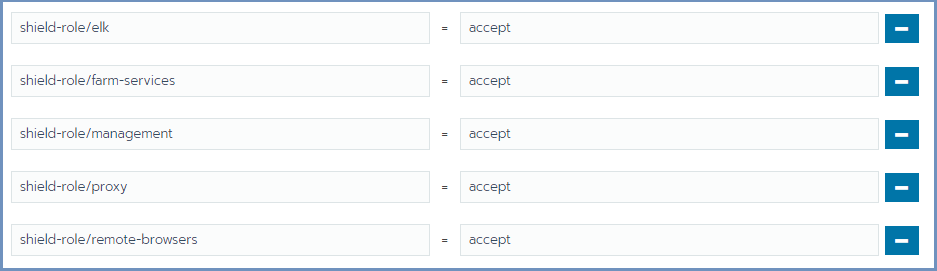
In the Edit Node dialog, expand the Labels section and add the desired labels to the node. For each label, set the value
accept. The possible labels are:
Labels can be added manually, one by one, or using copy/paste for one or more lines of the following labels:
shield-role/management=accept
shield-role/proxy=accept
shield-role/elk=accept
shield-role/farm-services=accept
shield-role/remote-browsers=accept
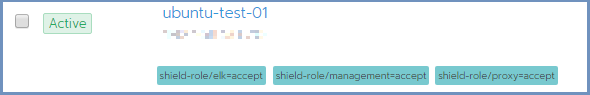
Press Save. The updated labels now appear on the node details:
The new Kubernetes cluster is now up and ready.
Cluster Management¶
Kubectl¶
Kubectl is used for running commands on Kubernetes clusters. For more details, see here.
Install Kubectl on the Linux Rancher Server machine. Run these commands:
curl -s -o install-kubectl.sh https://raw.githubusercontent.com/EricomSoftwareLtd/Shield/Rel-19.09.4/Kube/scripts/install-kubectl.sh
chmod +x install-kubectl.sh
./install-kubectl.sh
Update Kubeconfig¶
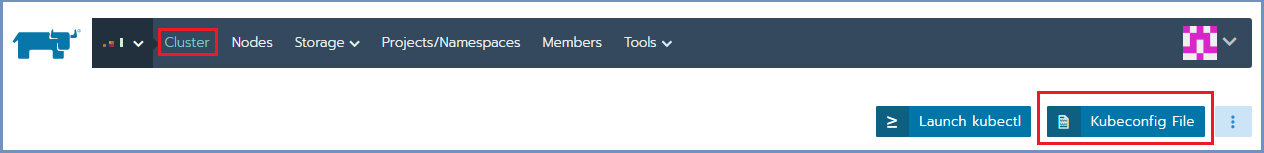
In Rancher, go to Cluster and select Kubeconfig File
Scroll down and select the Copy to Clipboard option. This will copy the content of the Kubeconfig file to the Clipboard.
On the Linux Rancher Server machine, edit (or create) the file named ~/.kube/config. Paste the clipboard content to the file.
Check that kubectl is configured properly (client and server):
kubectl version
The expected outcome is similar to:
Client Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"14", GitVersion:"v1.14.3", GitCommit:"5e53fd6bc17c0dec8434817e69b04a25d8ae0ff0", GitTreeState:"clean", BuildDate:"2019-06-06T01:44:30Z", GoVersion:"go1.12.5", Compiler:"gc", Platform:"linux/amd64"}
Server Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"13", GitVersion:"v1.13.5", GitCommit:"2166946f41b36dea2c4626f90a77706f426cdea2", GitTreeState:"clean", BuildDate:"2019-03-25T15:19:22Z", GoVersion:"go1.11.5", Compiler:"gc", Platform:"linux/amd64"}
Helm¶
Helm is an application manager, used to run applications on Kubernetes (e.g., Shield). Install Helm on the Linux Rancher Server machine.
To install Helm, run these commands:
cd ../
curl -s -o install-helm.sh https://raw.githubusercontent.com/EricomSoftwareLtd/Shield/Rel-19.09.4/Kube/scripts/install-helm.sh
chmod +x install-helm.sh
./install-helm.sh -c
Shield Repository¶
Note
Shield repository requires a valid password. Contact Ericom Shield Professional Services to get a valid password.
To add Shield repository to the Linux Rancher Server machine, run these commands (replace <PASSWORD> with the correct password):
curl -s -o add-shield-repo.sh https://raw.githubusercontent.com/EricomSoftwareLtd/Shield/Rel-19.09.4/Kube/scripts/add-shield-repo.sh
chmod +x add-shield-repo.sh
./add-shield-repo.sh -p <PASSWORD>
Verify that your repository is properly configured. Run:
helm search shield
The expected outcome is similar to
Note
If migrating from a legacy system, stop at this point and go to step 6 here.
Deploy Shield¶
Once the cluster is prepared and all the nodes in it include the required labels, Shield can be deployed. Run these commands to deploy Shield:
curl -s -o deploy-shield.sh https://raw.githubusercontent.com/EricomSoftwareLtd/Shield/Rel-19.09.4/Kube/scripts/deploy-shield.sh
chmod +x deploy-shield.sh
./deploy-shield.sh
Move Shield-Services To Default Project¶
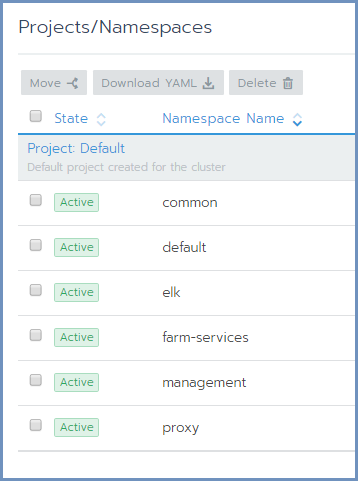
After Shield is deployed, the different namespaces (components) should be moved to be under the Default project, for easy display and access.
Under the cluster, there 5 namespaces: Management, Proxy, ELK, Farm Services & Common. There is also a default namespace, which exist by default under each cluster. The namespaces correspond with the Shield-Management, Shield-Proxy, Shield-Log, Farm Services and Common components respectively.
The Browsers component is a logical component, not represented by a namespace. This is because the browsers are created and managed by the Farm Services.
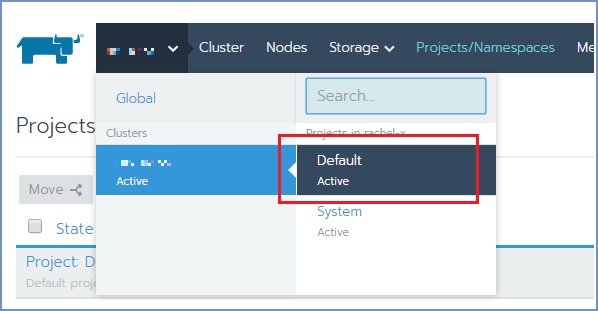
In Rancher, click on the Cluster. Then click on Projects/Namespaces. Select all Shield namespaces and click on the Move option
on top. Select Default and confirm. The Shield components are now displayed under the Default project.
Now, click on the cluster and select Default under the cluster name